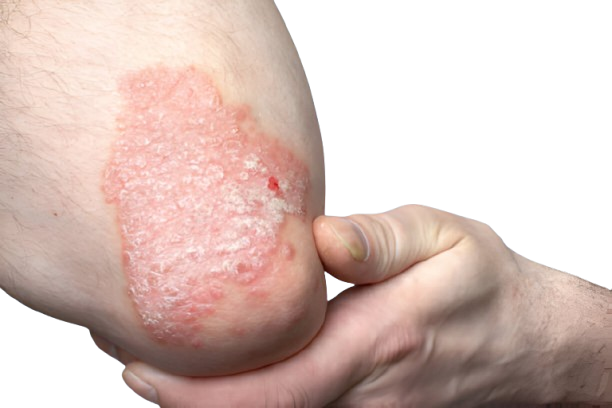
Understanding the Impact of Smoking on Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing red, itchy, and scaly patches to develop. While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors. One such environmental factor that has been shown to have a significant impact on psoriasis is smoking.
The Link Between Smoking and Psoriasis
Research studies have indicated that there is a clear correlation between smoking and the development and exacerbation of psoriasis. Smokers are more likely to develop psoriasis compared to non-smokers, and those with existing psoriasis may experience more severe symptoms if they continue to smoke.
Nicotine and Its Effects on Psoriasis
cotine and Its Effects on PsoriasisNicotine, a highly addictive compound found in cigarettes, is known to have detrimental effects on the skin. It can disrupt the immune system, triggering inflammation and potentially worsening existing psoriatic symptoms. Nicotine also narrows blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the skin and impairing its ability to heal.
Individuals who smoke and have psoriasis tend to have more severe symptoms and a higher prevalence of psoriatic arthritis, a condition that causes joint pain and swelling. Smoking can also diminish the effectiveness of certain psoriasis treatments, making it harder to manage the condition.
Secondhand smoke, which is the smoke exhaled by smokers or given off by burning tobacco, can also impact individuals with psoriasis. Being exposed to secondhand smoke may trigger flare-ups and worsen symptoms in people with the condition, even if they are not smokers themselves.
While the relationship between smoking and psoriasis is clear, the good news is that quitting smoking can lead to significant improvements in psoriatic symptoms. Studies have shown that individuals who quit smoking experience reduced skin inflammation, decreased severity of psoriasis, and better response to treatment.
If you have psoriasis and smoke, taking steps to quit can positively impact your overall health and well-being. Consider the following strategies to help you quit smoking .
Smoking can have a detrimental effect on psoriasis, exacerbating symptoms and making the condition more challenging to manage. By understanding the impact of smoking on psoriasis and taking steps to quit smoking, individuals can enhance their quality of life and reduce the severity of their psoriatic symptoms. Making the decision to quit smoking is a proactive step towards better skin health and overall well-being.
The link between lifestyle choices and psoriasis development
The relationship between smoking and psoriasis has been a topic of interest in the medical field for many years. Research has shown that smoking can have a detrimental effect on individuals with psoriasis. Smoking not only increases the risk of developing psoriasis but can also exacerbate existing symptoms and make the condition more difficult to manage.
Smoking and Psoriasis A Harmful Combination
Studies have demonstrated that smoking can trigger the onset of psoriasis in individuals who are genetically predisposed to the condition. The chemicals present in cigarettes can disrupt the immune system and increase inflammation in the body, leading to the development of psoriatic lesions. Moreover, smoking has been linked to the severity of psoriasis symptoms, with smokers often experiencing more frequent and severe flare-ups compared to non-smokers.
Nicotine and Psoriasis Flare-Ups
Nicotine, a key component of cigarettes, can also play a significant role in exacerbating psoriasis symptoms. Nicotine has been shown to stimulate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the body, which can worsen the inflammation associated with psoriasis. Additionally, nicotine can reduce the efficacy of certain psoriasis treatments, making it harder for individuals to manage their symptoms effectively.
While the relationship between smoking and psoriasis is concerning, there is some good news. Research indicates that quitting smoking can have a positive impact on individuals with psoriasis. By quitting smoking, individuals can reduce inflammation in their bodies, improve the effectiveness of psoriasis treatments, and decrease the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Lifestyle Changes for Psoriasis Management
In addition to quitting smoking, making other positive lifestyle changes can also benefit individuals with psoriasis. Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress levels, and getting regular exercise can all help improve psoriasis symptoms and overall well-being. It’s essential for individuals with psoriasis to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
Smoking can have a significant impact on the development and management of psoriasis. By quitting smoking and making other positive lifestyle changes, individuals with psoriasis can take control of their condition and improve their quality of life. It’s crucial for individuals with psoriasis to prioritize their health and well-being by adopting healthy habits and seeking support from healthcare professionals. By taking proactive steps to manage their condition, individuals with psoriasis can lead fulfilling and healthy lives.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, leading to the rapid growth of skin cells that results in red, scaly patches. While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, research has shown a strong association between smoking and the development and exacerbation of psoriasis symptoms.
Numerous studies have indicated that smoking can trigger and worsen psoriasis. Smoking increases oxidative stress in the body, which can lead to inflammation and skin cell damage, potentially worsening psoriasis symptoms. Furthermore, the chemicals in cigarette smoke can disrupt the immune system, causing it to attack healthy skin cells and triggering psoriasis flares.
The Impact of Smoking on Psoriasis Symptoms
Individuals with psoriasis who smoke tend to have more severe symptoms than non-smokers. Smoking can increase the risk of developing certain types of psoriasis, such as palmoplantar pustulosis, and can also reduce the effectiveness of psoriasis treatments. Smokers may experience more frequent and prolonged psoriasis flares, leading to discomfort and decreased quality of life.
Additionally, smoking has been linked to a higher risk of developing psoriatic arthritis, a type of arthritis that affects some individuals with psoriasis. Psoriatic arthritis causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, further impacting a person’s overall well-being. Quitting smoking is crucial for managing psoriasis and reducing the risk of complications associated with the condition.
Set a Quit Date: Choose a specific date to quit smoking and mark it on your calendar. Having a target date can help you mentally prepare for the change and increase your commitment to quitting.
Seek Support: Inform your friends, family, and healthcare providers about your decision to quit smoking. Surround yourself with a supportive environment to stay motivated and accountable throughout the quitting process.
Consider Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): NRT products, such as nicotine patches or gum, can help reduce nicotine withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable NRT option for you.
Explore Behavioral Therapies: Cognitive-behavioral therapy and counseling can assist you in addressing the psychological aspects of nicotine addiction and developing coping strategies to overcome triggers that may lead to smoking.
Stay Active Engage in regular physical activity to distract yourself from cravings and reduce stress, which can be a trigger for smoking. Exercise can also promote overall well-being and improve psoriasis symptoms.
Practice Stress-Relief Techniques Explore relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to manage stress levels effectively. Stress reduction is essential for preventing psoriasis flares and maintaining healthy skin.
Quitting smoking is paramount for individuals with psoriasis to alleviate symptoms, reduce the severity of flare-ups, and improve overall skin health. By implementing strategies for smoking cessation and seeking support from healthcare professionals and loved ones, individuals can embark on a journey towards better management of their psoriasis condition. Remember, every step taken towards quitting smoking is a step towards healthier skin and a brighter future free from the harmful effects of tobacco smoke.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by red, flaky patches on the skin that can be uncomfortable and sometimes even painful. Research has shown that certain lifestyle factors, such as smoking, can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms and potentially worsen the condition. However, the good news is that quitting smoking can have a positive impact on the progression of psoriasis.
Smoking Cessation A Step Towards Better Skin Health
When individuals with psoriasis quit smoking, they are taking a crucial step towards improving their skin health and overall well-being. Research suggests that quitting smoking can lead to a reduction in psoriasis symptoms and severity. By eliminating exposure to harmful toxins found in cigarettes, individuals can help alleviate inflammation in the body and reduce the risk of flare-ups.
Reduced Inflammation Smoking cessation can help lower inflammation levels in the body, which is beneficial for individuals with psoriasis. Lower levels of inflammation can lead to milder symptoms and less frequent flare-ups.
Improved Treatment Efficacy Quitting smoking can enhance the effectiveness of psoriasis treatments. Smoking can make certain treatments less effective, so eliminating this habit can help individuals better manage their condition.
Enhanced Skin Healing Smoking can slow down the skin’s natural healing process, making it harder for psoriatic lesions to heal. By quitting smoking, individuals can promote faster healing and potentially reduce scarring.
Seek Support Quitting smoking can be challenging, so it’s essential to seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, friends, and family members.
Stay Positive Maintaining a positive mindset throughout the quitting process can help individuals stay motivated and focused on their goal of improving their skin health.
Practice Healthy Habits Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques, can complement smoking cessation efforts and benefit overall skin health.
Quitting smoking can have a significant impact on the progression of psoriasis. By taking steps to eliminate this harmful habit, individuals with psoriasis can improve their symptoms, enhance treatment outcomes, and promote healthier skin. Embracing a smoke-free lifestyle is a positive choice that can lead to better skin health and an improved quality of life for those living with psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, causing red, scaly patches to appear. These patches can be itchy and painful, leading to discomfort for those living with the condition. While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, researchers have identified that inflammation plays a significant role in exacerbating the symptoms of psoriasis.
Inflammation is part of the body’s natural immune response to protect against harmful stimuli, such as pathogens or injuries. However, in conditions like psoriasis, the immune system becomes overactive, leading to persistent inflammation. This chronic inflammation triggers the rapid growth of skin cells, resulting in the thick, scaly patches characteristic of psoriasis.
Conclusion
Smoking can significantly impact psoriasis due to the harmful chemicals present in cigarettes that can exacerbate inflammation and trigger flare-ups. Lifestyle choices, including smoking, play a crucial role in the development and progression of psoriasis. Understanding the link between smoking and psoriasis is essential for individuals looking to manage their symptoms effectively.
Quitting smoking is a key strategy to improve psoriasis symptoms and overall health. By eliminating the harmful effects of smoking, individuals can reduce inflammation and potentially decrease the severity of their psoriasis flare-ups. Strategies for quitting smoking, such as seeking professional help, using nicotine replacement therapies, and finding alternative coping mechanisms, can support individuals in their journey towards a smoke-free life.
Moreover, the impact of smoking cessation on psoriasis progression should not be underestimated. Research suggests that quitting smoking can lead to significant improvements in psoriasis symptoms, including reduced severity and frequency of flare-ups. By addressing lifestyle factors like smoking, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing their condition and enhancing their quality of life.
It is crucial to recognize the role of inflammation in psoriasis exacerbation. Smoking can intensify inflammation in the body, making psoriasis symptoms more severe. By quitting smoking and adopting a healthier lifestyle, individuals can reduce inflammation levels and minimize the triggers that contribute to psoriasis flare-ups.
Making informed choices about lifestyle factors like smoking can have a profound impact on psoriasis management. By understanding how smoking affects psoriasis, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their symptoms and overall well-being. Quitting smoking, reducing inflammation, and prioritizing self-care are essential components of a comprehensive approach to managing psoriasis effectively. By addressing these key factors, individuals can work towards minimizing the impact of psoriasis on their daily lives and promoting long-term skin health.