Ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis are two distinct types of inflammatory arthritis that affect individuals differently. Understanding the characteristics, symptoms, and treatment options for these conditions is crucial for managing them effectively.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
This condition causes inflammation of the spinal joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. It commonly starts in the lower back and can progress to involve the entire spine. Ankylosing spondylitis can also affect other joints, tendons, and ligaments in the body. The pain and stiffness tend to improve with movement and exercise. In severe cases, ankylosing spondylitis can cause the vertebrae to fuse together, resulting in a rigid spine and loss of mobility.
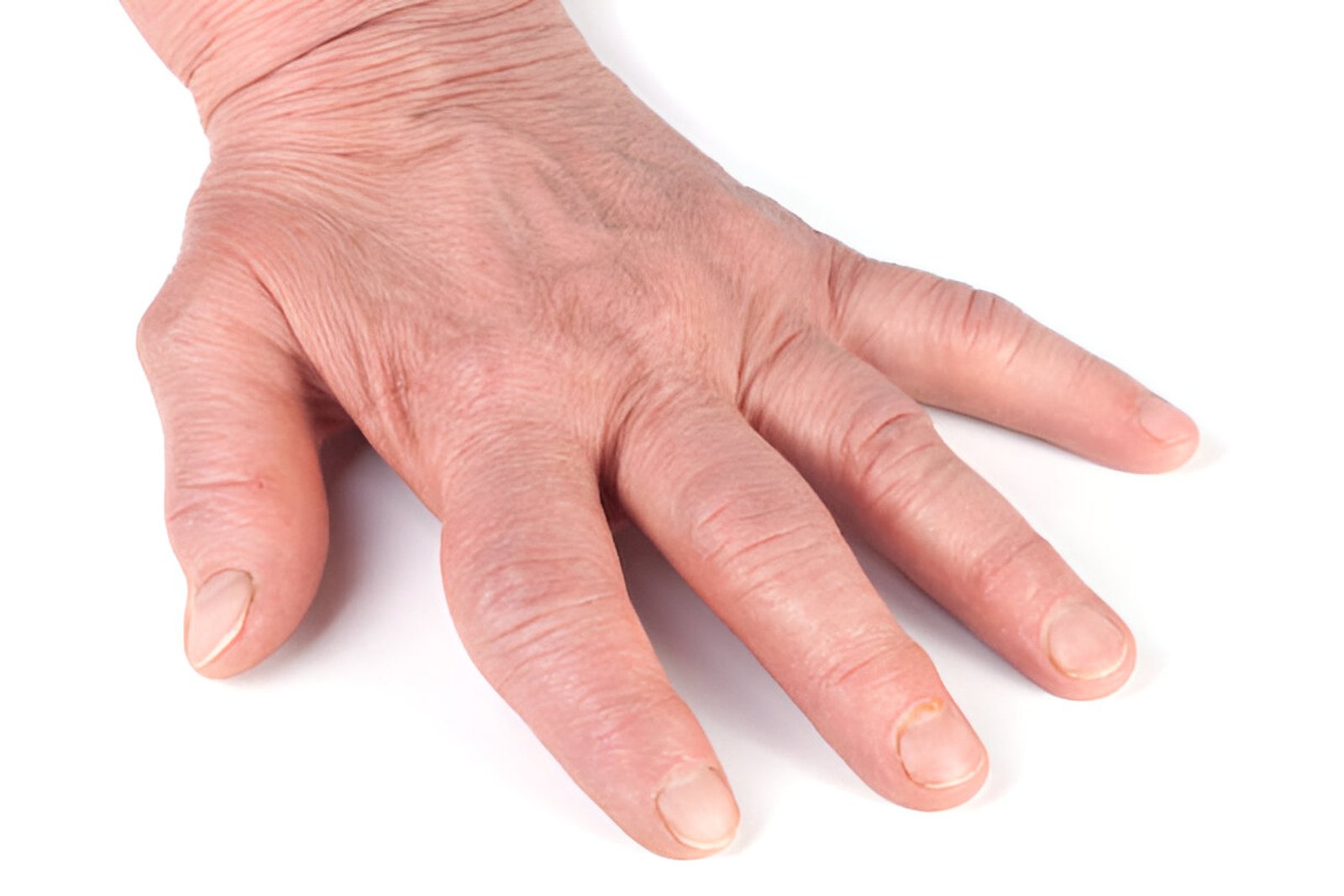
Rheumatoid Arthritis Unlike ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis can affect any joint in the body, including the hands, feet, wrists, and knees. The synovial membrane, which lines the joints, becomes inflamed, leading to joint damage and deformity over time.
Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may experience joint pain, swelling, and warmth, along with fatigue and general malaise. The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are typically symmetrical, meaning they affect the same joints on both sides of the body. In advanced stages, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to joint destruction and disability.
Key Differences
While both ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis are inflammatory arthritis conditions, they have several key differences. Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints, whereas rheumatoid arthritis can involve multiple joints throughout the body. Ankylosing spondylitis is more common in men and often appears in early adulthood, while rheumatoid arthritis is more prevalent in women and can develop at any age.
Treatment Options
The treatment for ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis aims to reduce pain, inflammation, and preserve joint function. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used to manage discomfort and stiffness in both conditions. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic therapies are often prescribed for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis to slow disease progression and prevent joint damage.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Physical therapy and regular exercise play a crucial role in managing both ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Strengthening exercises, stretching, and low-impact activities can help improve flexibility, reduce pain, and maintain mobility. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair joint damage and improve function.
Ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis are complex inflammatory arthritis conditions that require proper diagnosis and management. By understanding the differences between these two conditions and exploring the available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and maintain joint function. If you suspect you may have symptoms of either condition, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Key Differences in Symptoms and Diagnosis
Ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis are two types of autoimmune diseases that affect the joints and can cause significant pain and discomfort for those who suffer from them. While both conditions fall under the umbrella of arthritis, they have distinct differences in terms of symptoms and diagnosis.
Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine, leading to inflammation of the vertebrae. The hallmark symptom of this condition is back pain and stiffness that worsens over time. This pain is often worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity and can improve with movement. In advanced cases, ankylosing spondylitis can cause the vertebrae to fuse together, resulting in a loss of mobility and an exaggerated forward stooped posture.
Other common symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis may include inflammation and pain in other joints such as the hips, shoulders, and knees. Fatigue, uveitis (eye inflammation), and difficulty expanding the chest due to restricted lung expansion are also seen in some individuals with this condition.
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms
On the other hand, rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, but can also involve other organs in the body. It typically manifests as symmetrical pain, swelling, and stiffness in multiple joints, primarily affecting the small joints of the hands and feet, but also affecting larger joints such as the knees, shoulders, and hips.
Unlike ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis can cause joint deformities due to the erosion of cartilage and bone. Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may also experience systemic symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite, and a general feeling of malaise.
Diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis can be hard to diagnose because the early symptoms aren’t always clear and can look like other health problems. To help make the diagnosis, a full medical history, physical exam, blood tests to look for inflammation, and imaging studies like X-rays and MRIs may be used. People who have ankylosing spondylitis may also have a genetic marker called HLA-B27, which adds to the confidence in the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
A combination of symptoms, physical examination findings, blood tests for specific antibodies like rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP), and imaging studies like X-rays and ultrasound typically lead to the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
While ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis are both chronic autoimmune diseases that affect the joints, they have unique symptoms and diagnostic criteria that differentiate them. Early detection and prompt treatment can help manage signs and improve the quality of life for individuals living with these conditions. If you suspect you may have either condition, it is essential to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
The differences in treatment approaches between Ankylosing Spondylitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis are significant.
Ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis are two distinct autoimmune conditions that affect the joints, often leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While both conditions fall under the umbrella of inflammatory arthritis, they have different pathophysiological mechanisms and treatment approaches. Understanding the differences in how ankylosing syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis manifest is crucial in determining the most effective treatment strategies for each condition.
Diagnosis and symptoms
To tell the difference between ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis, doctors use a combination of clinical exams, imaging studies, and lab tests. Ankylosing spondylitis mostly affects the spine and sacroiliac joints, causing inflammation that can cause the vertebrae to fuse over time. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is a systemic disease that mostly affects the synovial joints, causing swelling, pain, and possible joint deformities.
For people with severe rheumatoid arthritis that don’t get better with other medicines, targeted synthetic DMARDs like tofacitinib may be considered. Corticosteroids may also be used for short-term symptom relief during disease flares. Like for people with ankylosing spondylitis, physical therapy is very important for keeping their joints working well, their muscles strong, and their overall quality of life.
While ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis share some similarities in terms of joint inflammation and autoimmune origins, they require distinct treatment approaches tailored to their unique disease mechanisms. Early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and a multidisciplinary approach involving rheumatologists, physical therapists, and other healthcare providers are essential in effectively managing these chronic conditions and improving patients’ quality of life.
Living with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis can pose significant challenges for individuals dealing with these conditions. However, with the right lifestyle management strategies and coping mechanisms, it is possible to enhance the quality of life and alleviate some of the symptoms associated with these chronic illnesses.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation in the vertebrae that can lead to severe pain and stiffness. On the other hand, rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune condition that targets the joints, resulting in inflammation, pain, and potential joint damage over time.
Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Exercise helps to improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and maintain joint function. Low-impact activities such as swimming, yoga, and walking are excellent choices to stay active without putting too much strain on the joints.
Balanced Nutrition
A healthy and balanced diet plays a vital role in managing the symptoms of both ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fatty fish can help reduce inflammation in the body. Additionally, avoiding processed foods, excessive sugar, and saturated fats can aid in maintaining overall health.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic pain and dealing with a long-term condition can be mentally challenging. Practicing stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help individuals cope with the emotional toll of ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Seeking support from therapists, support groups, or counselors can also provide valuable assistance.
Adequate Rest and Sleep
Getting enough rest and quality sleep is essential for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Fatigue is a common symptom of these conditions, and prioritizing rest can help manage energy levels throughout the day. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, maintaining a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing excellent sleep hygiene can contribute to better sleep quality.
Medication Adherence
Following the prescribed treatment plan and taking medications as directed by healthcare providers is crucial for managing ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis effectively. Medications help reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and slow down disease progression. It is essential to communicate any concerns or side effects with healthcare professionals to make necessary adjustments to the treatment regimen.
By implementing lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, stress management techniques, prioritizing rest, and adhering to medication plans, individuals can effectively manage the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. It is essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of living with these chronic conditions.
. Ankylosing spondylitis mainly impacts the spine, leading to stiffness and fusion of the vertebrae, while rheumatoid arthritis targets the joints, resulting in swelling, deformity, and erosion of cartilage and bone. Both conditions can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life if not managed effectively.
Diagnosis and early detection
Early diagnosis is crucial in managing ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis effectively. Healthcare providers utilize a combination of medical history, physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging studies like X-rays and MRIs to diagnose these conditions. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and fatigue is essential for prompt intervention and disease management.
Advancements in Research
Researchers have recently made progress in understanding how ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis work. They are now looking into new ways to treat these conditions that target specific molecules and pathways that play a role in the inflammatory processes. Biologics, which are genetically modified proteins that target specific parts of the immune system, have changed the way these conditions are treated and made things better for many patients.
Lifestyle modifications and self-care
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle modifications and self-care play a significant role in managing ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, practicing excellent posture, and adequate rest are essential for joint health and overall well-being. Diet modifications such as following an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms.
Education and support for patients
Patient education and support are vital components of managing ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition, treatment options, and self-care strategies enables them to actively participate in their care and make informed decisions. Support groups, counseling, and online resources provide emotional support and a sense of community for individuals living with these chronic conditions.
Ongoing research and advancements in the understanding and treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis offer hope for improved outcomes and better quality of life for affected individuals. By incorporating a multidisciplinary approach that combines medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and patient education, healthcare providers can effectively manage these complex autoimmune disorders and help patients lead fulfilling lives despite their conditions.
Conclusion
Navigating the challenges posed by ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis requires a comprehensive understanding of these conditions. By recognizing the key differences in symptoms and diagnosis, individuals and healthcare professionals can effectively differentiate between the two diseases and formulate appropriate treatment plans. While medications play a crucial role in managing both ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis, it is essential to note that the treatment approaches vary significantly. Ankylosing spondylitis primarily focuses on reducing inflammation and managing symptoms, whereas rheumatoid arthritis treatment aims to suppress the immune system’s abnormal response.
Moreover, lifestyle modifications and coping strategies are integral parts of managing ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and adopting joint protection techniques can significantly improve quality of life for individuals with these conditions. Additionally, seeking emotional support, staying informed about the latest treatment options, and actively participating in shared decision-making with healthcare providers are essential components of coping with the challenges posed by these diseases.
As research in the field of rheumatology continues to advance, promising developments in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis offer hope for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for patients. From novel biologic therapies to personalized medicine approaches, the landscape of managing these conditions is evolving rapidly. By staying informed about the latest research findings and actively participating in clinical trials, individuals living with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis can contribute to the ongoing progress in the field and access cutting-edge treatment options.
In essence, while ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis present unique challenges, they also offer opportunities for growth, resilience, and empowerment. By fostering an interdisciplinary approach that encompasses medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, emotional support, and involvement in research endeavors, individuals can effectively manage these conditions and lead fulfilling lives. By raising awareness, advocating for improved access to care, and promoting a holistic understanding of ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis, we can work towards creating a more supportive and inclusive environment for those impacted by these diseases. Together, we can strive towards a future where all individuals affected by these conditions can live their lives to the fullest potential.