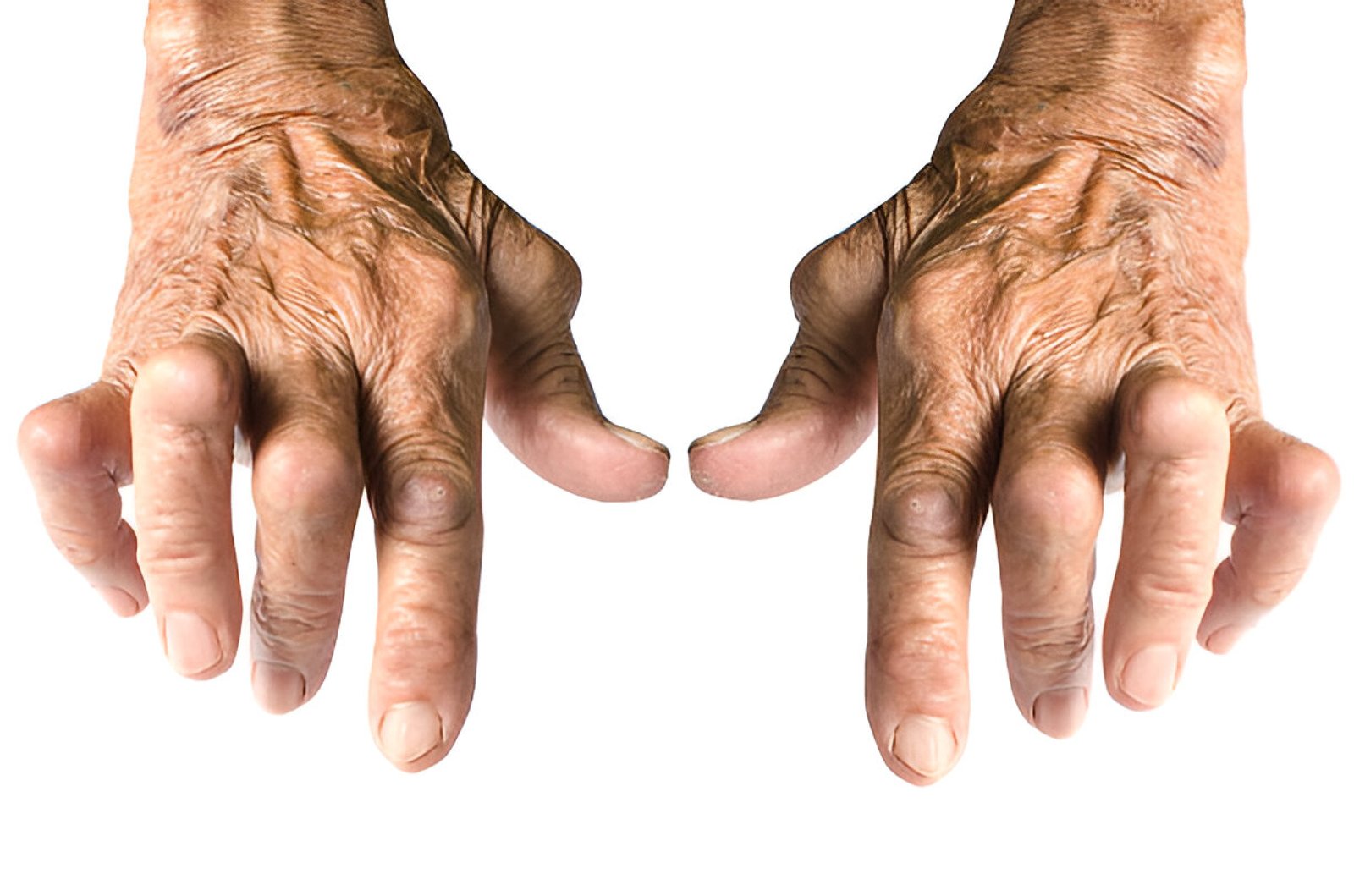
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation of the joints. As a progressive condition, it can lead to severe pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility. Nursing interventions play a crucial role in managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Nurses are essential members of the healthcare team, providing holistic care and support to patients with this condition.
Importance of nursing interventions
Nursing interventions for rheumatoid arthritis are vital in helping patients cope with the physical and emotional impact of the disease. Nurses collaborate with other healthcare professionals to create individualized care plans that address the specific needs of each patient. By focusing on symptom management, promoting self-care strategies, and offering emotional support, nurses can make a significant difference in the lives of individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis.
Pain Management Strategies
One of the primary goals of nursing interventions for rheumatoid arthritis is to help patients manage pain effectively. Nurses can educate patients about the importance of taking their medications as prescribed, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Additionally, nurses can teach patients about the use of heat and cold therapy, relaxation techniques, and gentle exercises to help alleviate pain and stiffness in the joints.
Education and Self-Care
Another essential aspect of nursing interventions for rheumatoid arthritis is patient education. Nurses play a key role in providing information about the disease process, potential complications, and treatment options. By empowering patients with knowledge, nurses enable them to take an active role in managing their condition. Nurses can also teach patients about the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate rest.
Support for daily activities
Since rheumatoid arthritis can affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities, nurses can provide practical support to help patients maintain their independence. This may include teaching patients adaptive techniques for tasks such as dressing, grooming, and cooking. Nurses can also collaborate with occupational therapists to assess the patient’s home environment and recommend modifications to improve safety and accessibility.
Emotional Support and Counseling
Living with rheumatoid arthritis can significantly impact a person’s mental health and emotional well-being. Nurses, trained to offer emotional support and counseling, can assist patients in navigating the emotional aspects of their condition. This includes offering a listening ear, encouraging open communication, and connecting patients with support groups or mental health services.
Nursing interventions for rheumatoid arthritis are essential in addressing the complex needs of patients with this chronic condition. By focusing on pain management, education, self-care, support for daily activities, and emotional well-being, nurses can make a positive impact on the lives of individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis. Their holistic approach to care helps patients achieve a better quality of life and manage their condition more effectively.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune illness characterized by continual infection of the joints. The immune device mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and, in severe instances, joint deformity. Understanding the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis is critical in developing powerful nursing interventions to control the signs and symptoms and improve sufferers’ tremendous lifestyles.
Role of Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis
In rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system produces inflammatory chemicals that target the synovium, which is the lining of the joints. These chemicals cause inflammation, leading to the characteristic symptoms of pain, swelling, and warmth in the affected joints. Over time, the chronic inflammation can damage the cartilage and bones within the joint, causing irreversible joint deformity.
Autoimmune Response
That’s why rheumatoid arthritis is called an autoimmune disease: the immune system attacks healthy tissue. In this case, the immune system thinks the synovium is a threat and starts to attack it. This autoimmune response causes the release of inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha and IL-6, which accelerate the inflammatory process.
Joint Degeneration
As rheumatoid arthritis progresses, the chronic inflammation leads to the degradation of the joint components. The synovium becomes thickened and inflamed, resulting in the formation of pannus – an abnormal tissue that erodes cartilage and damages the joint structures. Additionally, the inflammatory cytokines stimulate osteoclasts, which are cells responsible for breaking down bone tissue, leading to bone erosion and joint deformity.
Nursing Interventions for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Nurses play a crucial role in the management of rheumatoid arthritis by implementing various interventions to alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve overall well-being. Some key nursing interventions for rheumatoid arthritis include:
Patient Education
Educating patients about their condition, treatment options, and self-management strategies is essential in empowering them to take an active role in their care. Nurses can provide information about the importance of medication adherence, joint protection techniques, exercise programs, and stress management strategies to help patients better cope with the challenges of living with rheumatoid arthritis.
Pain Management
Pain is a significant symptom of rheumatoid arthritis that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Nurses can assess pain levels, administer pain medications as prescribed, and implement non-pharmacological pain management strategies such as heat and cold therapy, massage, and relaxation techniques to help patients.
Monitoring Disease Progression
In rheumatoid arthritis management, regular monitoring of disease activity and progression is critical. Nurses can assist in monitoring disease markers such as inflammatory markers (e.g., C-reactive protein), joint function, and disease activity scores to evaluate treatment effectiveness and adjust interventions as needed to achieve optimal outcomes for patients.
Collaborative Care
Collaboration with a multidisciplinary healthcare team, including rheumatologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and social workers, is essential in providing comprehensive care for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nurses can facilitate communication among team members, coordinate care plans, and ensure that patients receive holistic care that addresses their physical, emotional, and social needs.
Understanding the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis is essential for nurses to provide effective care and support to patients living with this chronic autoimmune disease. By implementing evidence-based nursing interventions and adopting a holistic approach to care, nurses can help patients manage symptoms, improve function, and enhance their quality of life despite the challenges of living with rheumatoid arthritis.
Medication Management for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
.It causes pain, inflammation, and stiffness, leading to decreased mobility and quality of life for those affected. Nursing interventions play a crucial role in managing the symptoms of RA and improving the overall well-being of patients. Medication management is a key aspect of RA treatment, involving a range of strategies to help patients better cope with the condition.
Monitoring and assessing medication efficacy
Nurses are responsible for monitoring and assessing the efficacy of the medications prescribed to patients with RA. This involves regularly evaluating the patient’s symptoms, functionality, and overall well-being to determine whether the current treatment plan is working effectively. Nurses need to communicate closely with patients to gather feedback on their medication experience and report any concerns to the healthcare team for further evaluation and adjustment of the treatment plan.
Managing Medication Side Effects
Another essential aspect of medication management for RA patients is helping them cope with potential side effects. Nurses should educate patients about common side effects associated with RA medications and provide strategies for managing them. This may include lifestyle modifications, alternative medications, or referral to other healthcare professionals for additional support. By addressing medication side effects proactively, nurses can help patients adhere to their treatment plan and improve their quality of life.
Promoting Adherence to Medication Regimens
Adherence to medication regimens is critical for the successful management of RA. Nurses play a key role in promoting adherence by providing ongoing support, education, and resources to help patients stay on track with their treatment plan. This may involve developing personalized medication schedules, using pill organizers, or setting reminders to help patients take their medications as prescribed. By fostering a partnership with patients and involving them in their care, nurses can enhance medication adherence and ultimately improve treatment outcomes.
Nursing interventions for rheumatoid arthritis focus on medication management as a cornerstone of treatment. By providing medication education, monitoring efficacy, managing side effects, and promoting adherence, nurses can empower patients to better cope with their condition and improve their quality of life. Through a patient-centered approach, caregivers can make a significant difference in the lives of individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the joints, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It is essential to have a multifaceted approach to managing this condition, which often includes a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and various therapies. Among these interventions, physical therapy plays a crucial role in improving the quality of life for individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Importance of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is an integral part of the treatment plan for rheumatoid arthritis. It focuses on improving joint function, reducing pain, and increasing mobility through a variety of exercises and techniques. A skilled physical therapist can create a customized exercise program tailored to the individual’s specific needs and limitations. These exercises aim to strengthen the muscles around the joints, improve flexibility, and enhance overall physical function.
Benefits of Physical Therapy
Pain Management: Physical therapy can help alleviate rheumatoid arthritis pain by using techniques such as heat and cold therapy, ultrasound, and manual therapy to reduce inflammation and discomfort.
Improved Range of Motion: Through targeted exercises, physical therapy can help increase the range of motion in affected joints, allowing individuals to perform daily tasks with greater ease.
Joint Protection: Physical therapists educate patients on how to protect their joints during everyday activities, preventing further damage and reducing the risk of complications.
Muscle Strengthening: Strengthening the muscles around the affected joints is crucial in providing support and stability, which can help relieve stress on the joints and improve function.
Enhanced Functionality: By addressing mobility issues and physical limitations, physical therapy aims to enhance overall functionality and quality of life for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
Types of Physical Therapy Interventions
Therapeutic Exercises: These include range-of-motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and aerobic conditioning to improve joint function and overall endurance.
Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage, mobilization, and manipulation are used to reduce pain, improve joint mobility, and enhance circulation.
Joint Protection Techniques: To minimize joint stress, physical therapists provide guidance on ergonomic principles, joint protection strategies, and adaptive equipment.
Education and Counseling: Patients receive valuable education on self-management techniques, lifestyle modifications, and coping strategies to better manage their condition.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the comprehensive management of rheumatoid arthritis. By focusing on pain management, improving range of motion, protecting joints, strengthening muscles, and enhancing overall functionality, physical therapy helps individuals with rheumatoid arthritis lead more active and fulfilling lives. Consult a healthcare professional to develop a personalized physical therapy plan that aligns with your specific needs and goals in managing rheumatoid arthritis.
Lifestyle modifications to support rheumatoid arthritis management
Lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in supporting individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. These modifications can significantly impact disease management and overall well-being. By incorporating specific changes to daily routines and habits, people can improve their symptoms, reduce inflammation, and enhance their quality of life. Let’s explore some effective lifestyle modifications that can support the management of rheumatoid arthritis.
Regular Exercise Routine
Engaging in regular physical activity is vital for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Exercise helps maintain joint flexibility, strengthen muscles, and improve overall joint function. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga are excellent choices for those with arthritis. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or a physical therapist to determine the most suitable exercise regimen based on individual needs and limitations.
Balanced Diet
A well-balanced diet plays a significant role in managing rheumatoid arthritis. Certain foods can help reduce inflammation and improve joint health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit individuals with arthritis. Additionally, antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables help combat oxidative stress in the body. Limiting processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats is also crucial for managing arthritis symptoms.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can exacerbate rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and trigger disease flares. Therefore, incorporating stress management techniques is essential for overall well-being. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation. Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as hobbies, spending time in nature, or listening to music, can also contribute to stress reduction.
Adequate Rest and Sleep
Proper rest and sleep are essential for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Fatigue is a common symptom of the condition, and inadequate rest can worsen overall health. Creating a sleep-conducive environment, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and practicing good sleep hygiene habits can improve the quality of sleep. Additionally, incorporating short rest periods throughout the day can help manage fatigue and prevent overexertion.
Joint Protection Techniques
Protecting the joints from unnecessary stress and strain is crucial for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Implementing joint protection techniques during daily activities can help reduce pain and prevent further damage. Simple strategies such as using assistive devices, maintaining proper posture, avoiding repetitive motions, and taking regular breaks during activities can protect the joints and improve overall function.
Lifestyle modifications are integral to supporting the management of rheumatoid arthritis. By incorporating regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, prioritizing rest and sleep, and implementing joint protection techniques, individuals can improve their symptoms and enhance their quality of life. Consulting with healthcare providers and specialists can help tailor these lifestyle adjustments to meet individual needs and optimize overall well-being.
Conclusion
The comprehensive care of patients with rheumatoid arthritis involves a multidisciplinary approach that puts nursing interventions at the forefront. Nurses play a crucial role in not only providing direct patient care but also in educating, supporting, and empowering patients to manage their condition effectively. By understanding the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis and being actively involved in medication management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications, nurses can significantly impact the overall well-being and quality of life of patients living with this chronic autoimmune disease.
Nurses are well-positioned as frontline healthcare providers to implement nursing interventions that focus on pain management, joint protection, and functional independence for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. By conducting thorough assessments, collaborating with other healthcare professionals, and developing individualized care plans, nurses can address the unique needs and challenges that each patient faces. Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment regimens, educating patients on self-care strategies, and providing ongoing support are all critical components of nursing care for rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Understanding the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis is fundamental for nurses to deliver optimal care. By recognizing the inflammatory nature of the disease and its impact on the joints, tissues, and organs, nurses can tailor interventions to target disease progression and maximize symptom relief. Educating patients about rheumatoid arthritis’s autoimmune nature and the importance of adhering to prescribed treatments can help improve treatment outcomes and promote patient empowerment in self-management.
Medication management is a critical aspect of rheumatoid arthritis care, and nurses play a vital role in ensuring patients understand their medications, adhere to prescribed regimens, and report any adverse reactions or changes in symptoms. By monitoring medication effectiveness, managing side effects, and collaborating with healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as needed, nurses contribute significantly to the overall well-being of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Physical therapy is an essential component of rheumatoid arthritis treatment, aiming to improve joint function, maintain mobility, and enhance overall quality of life. Nurses can support patients in accessing and adhering to physical therapy programs, monitoring progress, and addressing any concerns or barriers that may arise during rehabilitation. By promoting the benefits of physical therapy, encouraging regular exercise, and emphasizing the importance of joint protection techniques, nurses can help patients with rheumatoid arthritis achieve better functional outcomes and improved quality of life.
Lifestyle modifications are key to supporting rheumatoid arthritis management and optimizing overall health and well-being. Nurses can educate patients on the importance of balanced nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, adequate rest, and smoking cessation to help minimize disease activity, reduce joint inflammation, and enhance overall quality of life. By empowering patients to make healthy lifestyle choices and providing ongoing support and guidance, nurses can positively influence the long-term outcomes and prognosis of individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis.
Nursing interventions for rheumatoid arthritis encompass a holistic approach to patient care that addresses the physical, emotional, and psychosocial aspects of the disease. Through compassionate and evidence-based care, nurses play a pivotal role in supporting patients with rheumatoid arthritis in managing their symptoms, improving their function, and living well with their condition.