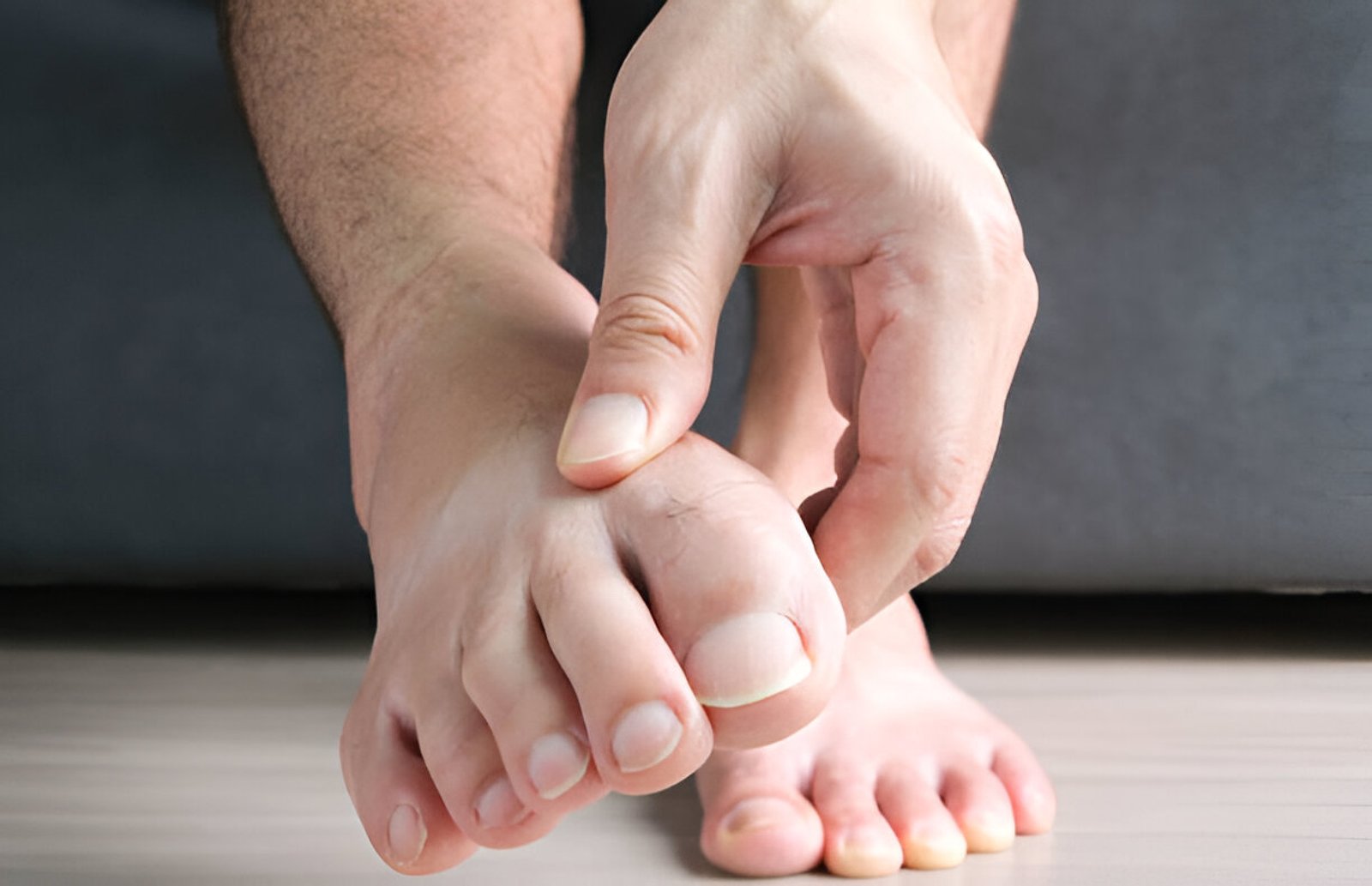
The body exhibits symptoms of elevated levels of uric acid.
High uric acid levels in the body, also known as hyperuricemia, occur when there’s an excess of uric acid in the blood. This can result in numerous wellness problems, with signs ranging from mild to severe. Understanding the preliminary indications of high uric acid levels is essential for timely intervention and administration.
Look out for early signs and symptoms.
Joint pain is one of the main symptoms of high uric acid levels, particularly in the joints of the big toe. This problem, known as gout, can trigger unexpected and serious pain, inflammation, and swelling in the affected joint. Gout strikes typically occur at night and can be debilitating.
Swelling: High uric acid levels can cause joints to swell, making them tender and sensitive to touch. The swelling is brought on by the development of uric acid crystals in the damaged area, triggering swelling and pain.
Ligament Pain: Tendons can likewise be influenced by elevated uric acid degrees, leading to pain. Ligament pain may manifest as rigidity, pain, or aching in the affected area, influencing mobility and adaptability.
Red or Purple Skin: Skin changes, such as inflammation or purplish discoloration, can occur in people with high uric acid degrees. These skin manifestations are frequently linked to gout attacks and may be accompanied by heat and extreme discomfort.
Added Signs, Symptoms, and Difficulties
Kidney Stones: High uric acid levels can contribute to the development of kidney stones, which can trigger intense discomfort. People with a history of kidney stones should be especially attentive regarding their uric acid levels.
Tiredness: Elevated uric acid levels can cause feelings of tiredness and general despair. This can have an impact on daily tasks and overall quality of life, making it critical to address the root cause of high uric acid levels.
Minimal Variety of Motion: Joint stiffness and decreased variety of movement may occur in individuals with elevated uric acid levels. This can make it difficult to perform routine jobs and tasks, influencing physical features and wheelchairs.
When to Seek Clinical Interest
If you experience any one of the symptoms discussed above, specifically recurrent joint pain, swelling, or skin changes, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider for an appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help prevent complications associated with high uric acid levels and boost general wellness and health.
Monitoring and handling
Gout
levels through lifestyle alterations, nutritional changes, and drugs can help stop the progression of signs and symptoms and reduce the threat of issues. By understanding the very early indicators of high uric acid levels and looking for prompt clinical recommendations, individuals can take positive steps in the direction of much better health and lifestyle.
Risk Factors Associated with Increased Uric Acid Levels
Raised uric acid degrees, also known as hyperuricemia, can cause a variety of health problems, including gout pain, kidney stones, and, in more severe cases, kidney illness. Understanding the danger variables related to high uric acid degrees can help people take proactive actions to handle their health and wellness properly.
Genetic Tendency
Genetics plays an important role in establishing a person’s chance of having elevated uric acid levels. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition that increases their susceptibility to this condition. If there is a family history of gout or high uric acid levels, there is a higher danger of experiencing comparable issues.
Diet Plan: High in Purines
Purines are natural substances found in certain foods that break down into uric acid in the body. Consuming a diet high in purine-rich foods such as red meat, body organ meats, seafood, and certain vegetables like mushrooms and asparagus can boost uric acid levels. Limiting your intake of these foods can help maintain uric acid levels.
Weight problems and an inactive lifestyle
Being obese or overweight is a considerable risk factor for elevated uric acid levels. Excess body weight and a less active lifestyle can cause inadequate uric acid production and excretion in the body. Participating in regular physical activity and keeping a healthy weight can decrease the risk of developing hyperuricemia.
Dehydration
Insufficient liquid consumption can lead to dehydration, which, subsequently, can contribute to elevated uric acid levels. Appropriate hydration is crucial for the kidneys to efficiently filter and eliminate uric acid from the body. People can help prevent uric acid accumulation in the bloodstream by staying well-hydrated.
Chronic health issues
Certain underlying health problems can raise the danger of elevated uric acid levels. Conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, metabolic disorders, and chronic kidney illness can interrupt the body’s balance of uric acid. Handling these wellness conditions through appropriate therapy and lifestyle adjustments is essential to preventing issues related to high uric acid levels.
Drugs
Some medications can hinder the body’s ability to manage uric acid levels. Medicines such as diuretics, low-dose aspirin, and immunosuppressants can possibly elevate uric acid levels as a side effect. It is essential for people taking these medications to check their uric acid levels frequently and consult with a doctor if necessary.
Acknowledging the risks associated with raised uric acid levels is critical to preventing problems such as gout pain and kidney stones. By dealing with these risk variables through lifestyle alterations, nutritional changes, proper hydration, and medical management, people can effectively lower their uric acid levels and decrease the danger of associated health problems. If you presume you have high uric acid levels, it is advisable to consult a health care expert for appropriate evaluation and guidance on managing your problem.
Effects of Untreated Uric Acid Accumulation
Uric acid is a waste product that is created when the body breaks down purines, compounds located in certain foods and beverages. Normally, the kidneys filter out uric acid, and it leaves the body via pee. Nevertheless, if the body generates too much uric acid or if the kidneys do not eliminate sufficient of it, it can cause a buildup of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. When hyperuricemia is left neglected, it can have different impacts on the body.
Effect on Joints and Gout
The development of gout is one of the main consequences of neglected uric acid accumulation. Gout arthritis is a kind of inflammatory arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals gather in the joints, triggering sudden and serious discomfort, swelling, and soreness. The first sign and symptom of gout arthritis is typically intense pain and swelling in the big toe, although it can impact various other joints such as the ankles, knees, arm joints, wrists, and fingers. Without proper therapy, gout attacks can become much more frequent and impact multiple joints, causing chronic gout arthritis and joint damage.
Kidney Rocks
The formation of kidney stones is another consequence of unattended high uric acid levels. Uric acid crystals can build up in the kidneys and integrate with other substances to develop stones. These stones can vary in dimension and may cause severe pain as they make their way through the urinary tract. In addition to discomfort, other signs of kidney stones include blood in the urine, constant peeing, and problem peeing. Chronic kidney stones can impair kidney function and cause problems that would otherwise be managed effectively.
Cardiovascular Risks
High levels of uric acid have actually been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Research has shown that people with hyperuricemia are more likely to develop conditions such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and stroke. Uric acid might contribute to the development of these conditions by causing swelling, endothelial disorder, oxidative stress, and anxiety. Individuals who deal with and manage elevated uric acid levels may reduce their risk of cardiovascular complications.
Metabolic Disorder
Untreated uric acid buildup has been linked to metabolic syndrome, a collection of conditions that increase the threat of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolic disorder is identified by variables such as abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, raised blood sugar degrees, and unusual lipid profiles. A research study recommends that hyperuricemia may contribute to the growth of metabolic abnormalities and insulin resistance, further underscoring the importance of monitoring and resolving uric acid levels.
Unattended uric acid buildup can have considerable effects on general health and wellness, ranging from joint pain and kidney stones to cardio-vascular risks and metabolic disturbances. Individuals with hyperuricemia must work closely with their doctor to manage their uric acid levels through lifestyle modifications, medication, and dietary adjustments. By attending to uric acid buildup proactively, people can minimize the threat of issues and boost their quality of life.
Dietary and lifestyle changes are necessary to manage uric acid levels.
Uric acid is an all-natural waste item that forms when the body breaks down purines, which are materials found in particular foods. When the body produces excessive uric acid or if the kidneys do not eliminate sufficient of it, high levels can accumulate in the blood, leading to a problem referred to as hyperuricemia. This can cause crystals to form in the joints, causing discomfort and swelling—a condition called gout. Taking care of uric acid levels via dietary and lifestyle modifications is essential to preventing gout attacks and improving overall health.
Limit purine-rich foods.
Purine-rich foods, such as organ meats, red meat, fish and shellfish, and particular veggies like spinach and mushrooms, can contribute to increased uric acid levels in the body. Restricting consumption of these foods can help manage uric acid levels. Rather, opt for low-purine alternatives like low-fat milk products, tofu, nuts, and seeds.
Remain Hydrated
Consuming an adequate quantity of water throughout the day is crucial for weakening uric acid and helping the kidneys flush it out of the body. The purpose is to consume a minimum of 8–10 glasses of water daily to stay moisturized and support kidney function in controlling uric acid levels.
Select complex carbs.
Complex carbs like entire grains, fruits, and vegetables are beneficial for people with high uric acid levels. These foods are high in fiber and low in purines, making them a healthier option to help manage uric acid and overall health.
Maintain a healthy weight.
Being obese or overweight is a risk factor for high uric acid levels and gout pain. By preserving a healthy and balanced weight with a balanced diet and routine physical activity, you can decrease the pressure on your joints and reduce the threat of uric acid buildup.
Alcohol and sugary beverages are limited.
Alcohol and sugary drinks, specifically those sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup, can contribute to increased uric acid levels in the body. Restricting or staying away from these drinks can help avoid spikes in uric acid and reduce the risk of gout pain.
Boost vitamin C consumption.
Vitamin C has been shown to reduce uric acid levels in the body. Including foods abundant in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and kiwis, can be valuable for individuals wanting to manage their uric acid levels normally.
Making nutritional and lifestyle changes is critical to managing uric acid levels and reducing the risk of gout attacks. By complying with a well-balanced diet, staying moisturized, maintaining a healthy weight, and making smart food choices, you can sustain total health, wellness, and well-being while keeping uric acid levels in check. The importance of routine tracking and checking for uric acid is significant. We are conducting routine surveillance and checking for Uric Acid.
Recognizing Uric Acid Degrees
Uric acid is a waste product created by the body during the breakdown of purines, which are compounds found in specific foods and drinks. Generally, uric acid dissolves in the blood, travels to the kidneys, and is secreted through pee. Nonetheless, raised levels of uric acid can bring about various health problems, including gout arthritis, kidney stones, and kidney conditions.
The importance of monitoring the levels of uric acid
Routine tracking and screening of uric acid levels are essential for individuals in jeopardy of developing conditions connected to high uric acid degrees. Early detection of raised uric acid levels can help prevent the onset of gout or other health issues. Surveillance is particularly crucial for people with a family history of gout pain, kidney illness, or those with specific clinical problems like diabetes or hypertension.
Common Symptoms of High Uric Acid
Regular screening for uric acid levels is crucial because high uric acid levels typically do not initially present any obvious signs and symptoms. However, as uric acid levels continue to rise, the following symptoms may begin to show up:
Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals gather in the joints, resulting in sudden and severe pain, inflammation, and swelling. Gout typically affects the joint at the base of the big toe, but it can also occur in other joints.
Joint Pain: Even before a gout attack, high levels of uric acid can cause joint discomfort. The discomfort might initially be mild and periodic, but it can worsen over time if left untreated.
Kidney Rocks: Uric acid can crystallize in the kidneys, causing kidney stones to form. These stones can cause intense pain in the back, abdominal area, or side, along with other symptoms such as nausea and blood in the pee.
Tiredness: Individuals with raised uric acid degrees may experience inexplicable tiredness or weakness. This symptom can have a significant impact on daily tasks and quality of life.
The Role of Normal Checking
Given the quiet nature of high uric acid degrees, regular screening is vital for keeping track of changes in degrees gradually. Blood examinations are typically used to determine uric acid levels in the body. Based on the test results, healthcare providers can recommend appropriate lifestyle modifications, medications, or treatments to help handle uric acid levels and avoid problems.
Changes in Lifestyle to Manage Elevated Uric Acid Levels
Along with tracking and screening, particular lifestyle alterations can help individuals maintain healthy and balanced uric acid levels. These consist of:
Keeping a Healthy and Balanced Diet: Restricting purine-rich foods such as red meat, organ meats, and particular sorts of seafood can help reduce uric acid levels.
Remaining Hydrated: Drinking an ample quantity of water daily can help clear out excess uric acid from the body.
Handling Weight: Preserving a healthy and balanced weight and avoiding crash diets can protect against spikes in uric acid degrees.
Regular surveillance and testing of uric acid levels play a vital role in preventing the growth of gout pain, kidney stones, and other associated conditions. By remaining aggressive and functioning very closely with healthcare providers, individuals can efficiently manage their uric acid degrees and preserve overall health and wellness. Keep in mind that early detection is key to attending to any potential issues connected to high uric acid levels.
Conclusion
Recognizing the initial signs of uric acid is critical for its early detection and management. Identifying indicators such as joint discomfort, inflammation, and swelling can encourage people to seek medical attention and prevent further issues related to high uric acid levels. Understanding the threat variables associated with elevated uric acid, such as dietary choices, obesity, and genes, encourages people to make more informed decisions about their health.
Moreover, unattended uric acid accumulation can bring about extreme wellness concerns like gout, kidney stones, and kidney conditions. By acknowledging the results of neglected uric acid buildup, individuals can take aggressive steps to manage their levels through nutritional adjustments, hydration, and regular exercise. Foods that help lower uric acid degrees, such as cherries, olive oil, and leafy greens, can help maintain a healthy and balanced equilibrium.
Additionally, embracing a holistic approach that incorporates nutritional and lifestyle modifications is essential to handling uric acid levels successfully. Staying clear of purine-rich foods, restricting alcohol usage, and remaining moistened are crucial parts of a uric acid-friendly lifestyle. Engaging in normal exercise not only promotes overall wellness but also aids in regulating uric acid levels in the body.
Routine surveillance and screening for uric acid are important elements of preventive medical care. Setting up examinations with healthcare providers can help people track their uric acid levels over time and make necessary adjustments to their treatment strategies. By staying proactive and notified concerning their health and wellness status, individuals can control their well-being and decrease the threat of complications connected with raised uric acid.
Fundamentally, recognizing the signs, risk variables, and repercussions of high uric acid levels emphasizes the importance of positive monitoring. By making informed choices regarding diet, way of life, and normal monitoring, individuals can alleviate the effect of uric acid on their health and wellness. Encourage yourself with expertise, listen to your body, and prioritize your health.